Can you violate the First Amendment by blocking people from your Twitter account? According to the Knight First Amendment Institute, it’s possible if that account is @realDonaldTrump.
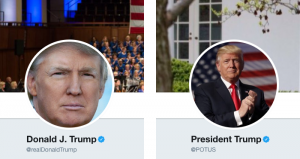 As we have mentioned before, Donald Trump’s Twitter habit has been a large part of his public persona in recent years. Unsurprisingly, his Twitter usage has continued to play a role in his presidency, at times even shaping the news cycle. In fact, the President’s tweets have garnered the attention of everyone from the writers at SNL to world leaders. The tweets even received a satirical “popup” library to commemorate Trump’s 140-character musings.
As we have mentioned before, Donald Trump’s Twitter habit has been a large part of his public persona in recent years. Unsurprisingly, his Twitter usage has continued to play a role in his presidency, at times even shaping the news cycle. In fact, the President’s tweets have garnered the attention of everyone from the writers at SNL to world leaders. The tweets even received a satirical “popup” library to commemorate Trump’s 140-character musings.
 Internet & Social Media Law Blog
Internet & Social Media Law Blog